Author: Amitabh Soni
In this blog post, I will walk you through the process of setting up a CI/CD pipeline for a Spring Boot banking application. This pipeline will automate the build, deployment, and integration processes using Jenkins, Docker, and GitHub. You will learn how to leverage a multi-node Jenkins architecture, shared libraries, and webhooks for automatic deployments.
Repository for this Project: https://github.com/Amitabh-DevOps/Springboot-BankApp
Use the
devbranch for the code related to this project.
Project Overview
This project involves creating a complete CI/CD pipeline that automates the deployment of a Spring Boot-based banking application. Here are the steps we will follow:
- Create AWS EC2 Instances to host Jenkins and Docker.
- Set up Jenkins to automate the CI/CD pipeline.
- Containerize the Spring Boot application using Docker.
- Integrate GitHub for automatic deployment triggered by code changes.
- Use a multi-node Jenkins setup to deploy the application on a development server.
- Create a Jenkinsfile for automated builds and deployment.
- Set up webhooks in GitHub to trigger Jenkins builds on code changes.
Steps to Implement the Project
To set up a Jenkins Master-Agent architecture on AWS, we will create two EC2 instances. The Jenkins Master instance will manage Jenkins, while the Jenkins Agent instance, with higher resources, will host and deploy the Spring bootapplication.
Step 1: Create Two AWS EC2 Instances
We’ll start by setting up two separate instances: one for the Jenkins Master and one for the Jenkins Agent.
- Log in to AWS:
Go to the AWS Console and log in. - Launch an EC2 Instance (Jenkins Master):
- Go to the EC2 Dashboard and click on Launch Instance.
- Select the Ubuntu 24.04 LTS AMI.
- Choose t2.micro for the Jenkins Master instance, eligible for the free tier.
- Configure Security Group:
- SSH (port 22) for remote access.
- HTTP (port 80) to access Jenkins through the browser.
- Click Review and Launch.
- Launch an EC2 Instance (Jenkins Agent):
- Repeat the above steps, but select t2.medium for the Jenkins Agent instance.
- Use the same key pair as used for the Jenkins Master.
Note: For simplicity and consistency, it’s best to use the same key pair for both instances. This enables both instances to be accessed with a single private key file (e.g.,
<your-key>.pem), which is useful for managing both servers in a DevOps environment.
Step 2: Connect to Each EC2 Instance
SSH into both instances using:
ssh -i <your-key>.pem ubuntu@<your-ec2-public-ip>Step 3: Update Each EC2 Instance
Ensure both instances are up-to-date by running:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yStep 4: Install Java on Both Instances
Jenkins requires Java, so install OpenJDK 17 on each instance:
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jre -y
java -versionStep 5: Install Jenkins (Only on Jenkins Master)
- Install dependencies:
sudo apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg - Add the Jenkins repository key:
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null - Add Jenkins to APT sources:
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian binary/ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null - Install Jenkins:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkins -y - Enable Jenkins to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable jenkins sudo systemctl start jenkins - Verify Jenkins status:
sudo systemctl status jenkins
Step 6: Install Docker on Both Instances
- Install Docker:
sudo apt install docker.io -y - Add Jenkins to the Docker group (on both instances):
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER - Refresh Docker group membership:
newgrp docker
Step 7: Install Docker Compose on Both Instances
sudo apt install docker-compose-v2 -y
docker --version
docker-compose --versionStep 8: Configure Jenkins Security Groups for Web Access
Edit the security group of your Jenkins Master instance:
- Go to the EC2 Dashboard, select Security Groups, and choose the security group associated with your EC2 instance.
- Click on Edit Inbound Rules and add a rule for Custom TCP Rule with port 8080.
- Access Jenkins in a web browser using
http://<your-ec2-public-ip>:8080.
Step 9: Retrieve Jenkins Admin Password
Retrieve the initial admin password:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordUse this password to complete the initial setup in Jenkins by following the on-screen instructions.
Step 10: Creating a Development Server from Jenkins Agent Instance to Deploy Spring boot bank App
To add a new node in Jenkins:
- Log in to Jenkins.
- Go to Manage Jenkins > Manage Nodes and Clouds.
- Click New Node:
- Node name: Enter a name for the Jenkins Agent (e.g.,
dev-server). - Choose Permanent Agent and click OK.
- Node name: Enter a name for the Jenkins Agent (e.g.,
- Configure Node Settings:
- Make sure to create a directory named bankapp on the agent machine
- Remote root directory:
/home/ubuntu/bankapp - Labels: Add
dev-server - Usage: Choose Only build jobs with label expressions matching this node.
- Under Launch method, select Launch agents via SSH:
- Host: Enter the PUBLIC IP of your Jenkins Agent instance.
- Credentials: Add credentials by selecting SSH Username with private key.
- Use ubuntu for the username.
- Add the private key associated with the key pair used for the Jenkins Agent EC2 instance.
- Click Save and connect to the Jenkins Agent.
Step 11: Set Up Docker Hub Credentials in Jenkins
- Go to Manage Jenkins > Security > Credentials > System > Global credentials (unrestricted) and click Add Credentials.
- Set Kind to Username with password.
- Add your Docker Hub username and password and save , for password generate Personal Access Token on DockerHub.
Step 12: Create a Shared Library Repository
- Create a GitHub Repository:
- Go to GitHub and create a new repository.
- Name it something like
Jenkins-shared-library. - Add a description, set it to Public or Private (based on your needs), and click Create Repository.
- Clone the Repository:
- Clone the repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/Amitabh-DevOps/Jenkins-shared-library.git - Navigate into the directory:
cd Jenkins-shared-library
- Clone the repository to your local machine:
- Set Up the Folder Structure:
- Create the
varsdirectory to store your shared library functions:mkdir vars - The structure should look like this:
Jenkins-shared-library/ └── vars/
- Create the
Step 13: Add .groovy Scripts
Inside the vars directory, create the following .groovy files.
clone.groovy
Handles code cloning from a Git repository:
def call(String url, String branch){
git url:url , branch:branch
}dockerbuild.groovy
Builds a Docker image:
def call(String imageName, String imageTag){
sh "docker build -t ${imageName}:${imageTag} ."
}dockerpush.groovy
Pushes a Docker image to Docker Hub:
def call(String credId, String imageName,String imageTag){
withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId:credId,
usernameVariable:"dockerHubUser",
passwordVariable:"dockerHubPass")]){
sh "docker login -u ${env.dockerHubUser} -p ${env.dockerHubPass}"
sh "docker image tag ${imageName}:${imageTag} ${env.dockerHubUser}/${imageName}:${imageTag}"
sh "docker push ${env.dockerHubUser}/${imageName}:${imageTag}"
}
}deploy.groovy
Deploys a Docker container:
def call(){
sh "docker compose down && docker compose up -d --build"
}Step 14: Commit and Push Changes
- Add and Commit the Files:
git add . git commit -m "Added shared library scripts for Jenkins pipeline." - Push to GitHub:
git push origin main
Step 15: Configure the Shared Library in Jenkins
- Access Jenkins:
- Go to Manage Jenkins > Configure System.
- Add Global Pipeline Library:
- Scroll to Global Pipeline Libraries and click Add.
- Fill in the details:
- Name:
Shared(matches@Library('Shared')in yourJenkinsfile). - Default Version:
main. - Retrieval Method:
Modern SCM. - Source Code Management:
- Select Git.
- Add the repository URL:
https://github.com/Amitabh-DevOps/Jenkins-shared-library.git - Add credentials if required (e.g., GitHub token or SSH key).
- Name:
- Save Configuration:
- Click Save.
Step 16: Create the Jenkinsfile on GitHub
In the GitHub main Application repository, create a Jenkinsfile containing the pipeline script:
@Library('Shared')_
pipeline{
agent {label 'dev-server'}
stages{
stage("Code"){
steps{
clone("https://github.com/Amitabh-DevOps/banking-app-project.git","dev")
echo "Code clonning done."
}
}
stage("Build"){
steps{
dockerbuild("bankapp-mini","latest")
echo "Code build bhi hogaya."
}
}
stage("Push to DockerHub"){
steps{
dockerpush("dockerHub","bankapp-mini","latest")
echo "Push to dockerHub is also done."
}
}
stage("Deplying"){
steps{
deploy()
echo "Deployment bhi done."
}
}
}
}
This script pulls the code from GitHub, builds and pushes a Docker image to Docker Hub, and deploys it on the Jenkins Agent instance.
- This script includes multiple stages: cloning the code from GitHub, building the Docker image, pushing it to Docker Hub, and deploying the container.
- This script allows to used shared library repo which is stored on my github profile
- used shared library repo : github.com/Amitabh-DevOps/Jenkins-shared-libraries
- Commit the Changes:
- Save and commit the
Jenkinsfileto your GitHub repository.
- Save and commit the
Step 17: Create a Jenkins Pipeline Job
- Create a New Job:
- From the Jenkins dashboard, click on New Item.
- Enter a name (e.g.,
Springboot bank CICD), select Pipeline, and click OK.
- Configure GitHub Integration:
- In the General section, check the GitHub project option.
- Provide the URL of your GitHub repository.
- Pipeline:
- Under Pipeline, select Pipeline script from SCM.
- Set SCM to Git and provide the Git repository URL.
- Choose the
devbranch and set Script Path toJenkinsfile.
Step 18. Set Up Webhooks for Automatic Deployment
To trigger the Jenkins pipeline automatically on code changes, set up webhooks in your GitHub repository.
- Go to GitHub Repository Settings:
- Navigate to your GitHub repository, and click on Settings.
- Set Up Webhooks:
- In the left sidebar, click on Webhooks and then Add webhook.
- Enter the Payload URL:
http://<your-ec2-public-ip>:8080/github-webhook/- Set Content type to default one and enable Just the push event.
- Click on Add webhook and wait for it to show a green tick, indicating successful setup.

Step 19. Build the Project in Jenkins
- Trigger the First Build:
- Go back to the Jenkins dashboard and click on the Build Now button for your pipeline job.
- This action will initiate the pipeline and deploy your Spring boot application.
- Access the Application:
- To allow incoming traffic to your application, go to your Jenkins Agent EC2 security group and add an inbound rule for port 8000.
- After the build completes successfully, visit your deployed Spring boot application at:
http://<your-ec2-public-ip>:8000 #Ip should be Jenkins agents & not master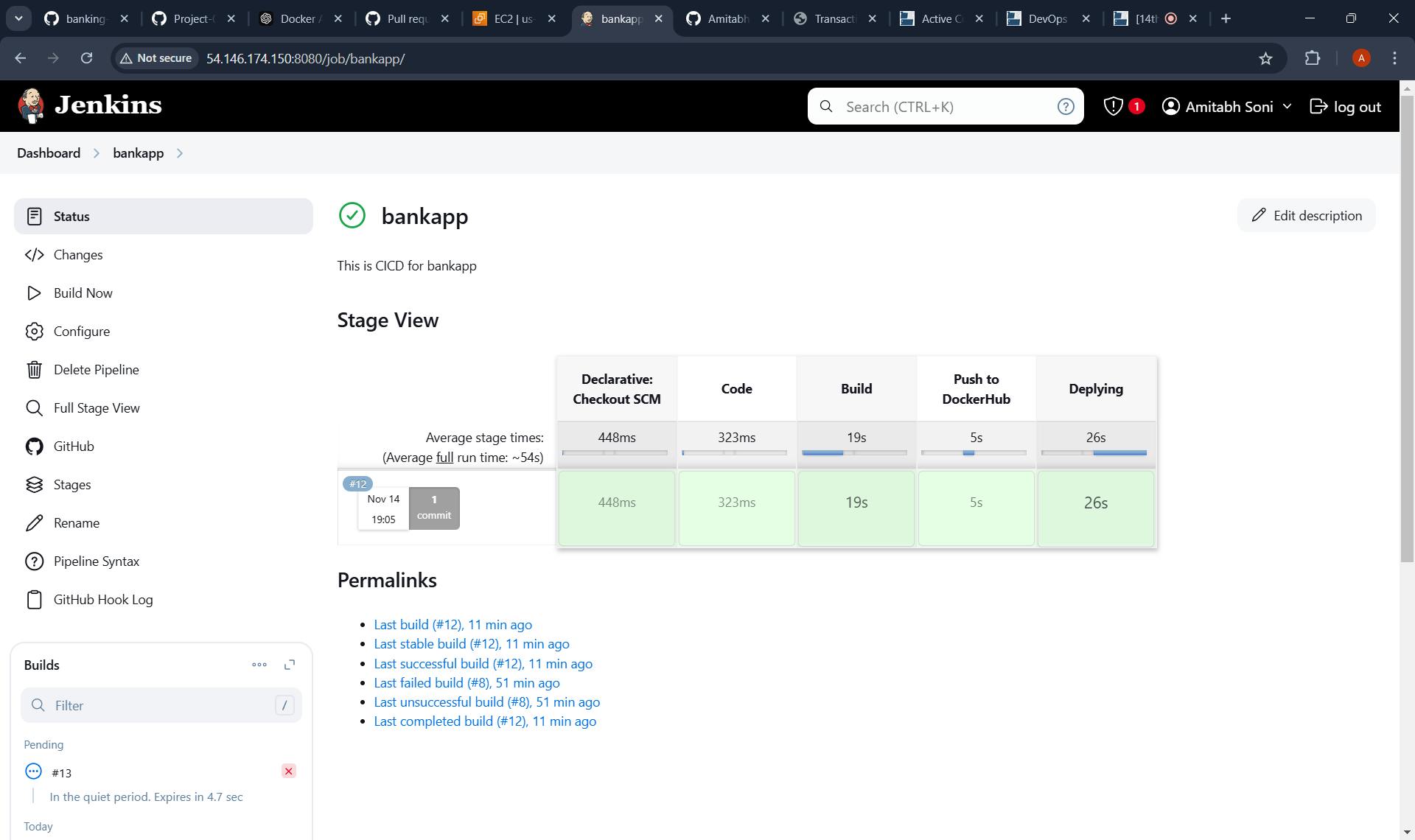
Step 20. Automatic Deployment
From this point on, any changes you make and push to the GitHub repository will automatically trigger Jenkins to run the pipeline, rebuild the Docker image, and redeploy the application. This completes the CI/CD setup for your Springboot bank Application.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you have successfully set up a CI/CD pipeline to automate the deployment of your Springboot bank Application using Jenkins, GitHub, and Docker, shared libraries, multinode agent etc. This setup not only simplifies the deployment process but also enhances productivity by ensuring that every code change is automatically tested and deployed.
Output Images of Project ( Which I have done while practicing CI/CD for this Project which ensure that it works properly)
- making changes on github to see it works properly or not :

- Checking if it triggers build on jenkins or not :

- Building the stages on Jenkins :

- It successfully builds the all stages :

- Checking the features of Application whether it is working or not :







- Adding some of a images that show lot of error to complete this project :





Author: Amitabh Soni
